The glycemic index chart is a valuable tool for individuals who are looking to make wise food choices and manage their blood sugar levels. It provides information on the effect different foods have on blood sugar levels, helping individuals understand which foods are high or low on the glycemic index scale.
Glycemic Index Chart
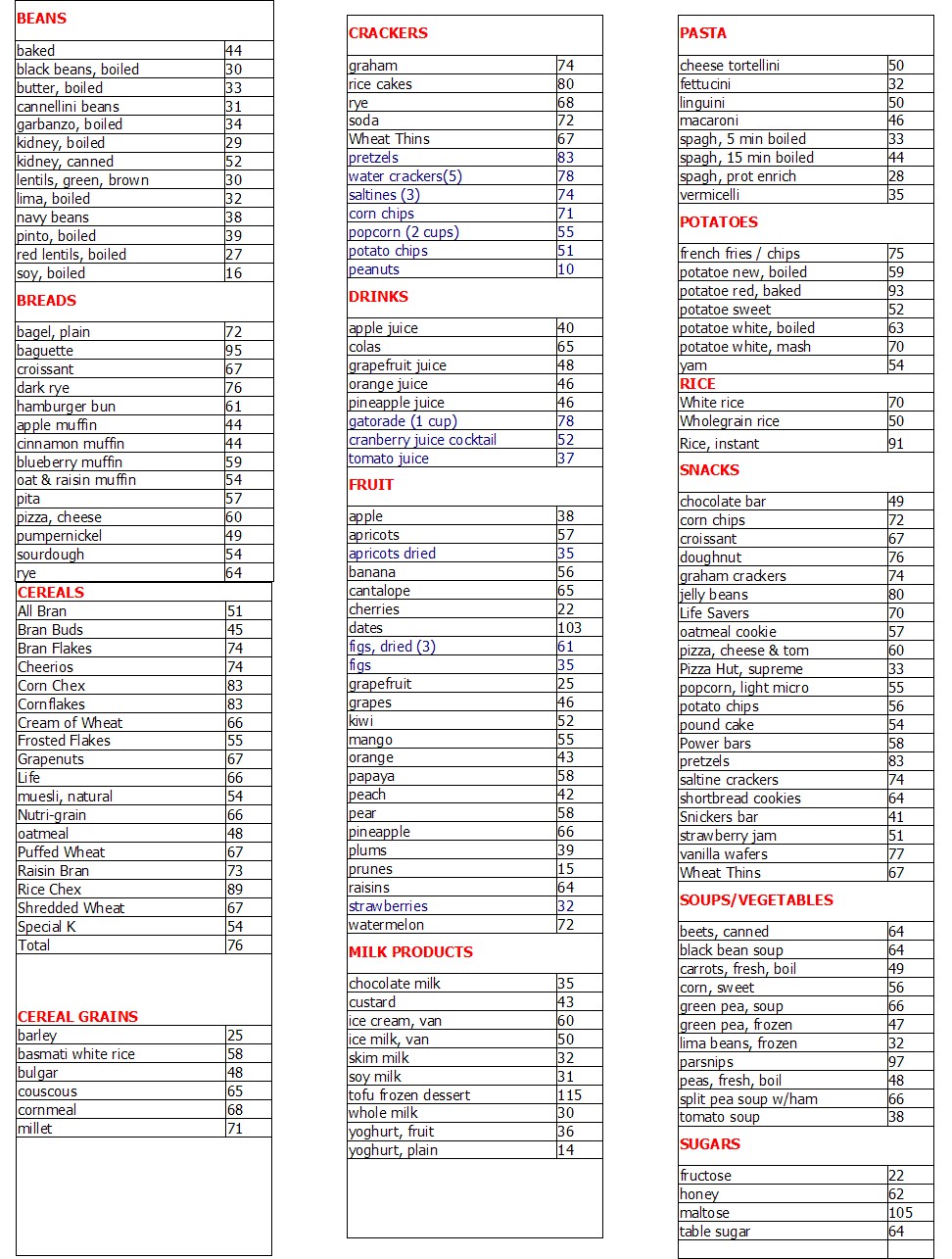 The glycemic index chart lists various foods and assigns them a number based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index value (55 or less) are digested and absorbed more slowly, causing a slower rise in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods with a high glycemic index value (70 or more) are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a quicker and higher spike in blood sugar levels.
The glycemic index chart lists various foods and assigns them a number based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index value (55 or less) are digested and absorbed more slowly, causing a slower rise in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, foods with a high glycemic index value (70 or more) are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a quicker and higher spike in blood sugar levels.
By referring to the glycemic index chart, individuals can make informed decisions about their food choices. This can be especially beneficial for those with diabetes or individuals who are trying to manage their weight. Choosing low glycemic index foods can help maintain stable blood sugar levels, prevent sudden spikes and crashes in energy, and promote overall health and well-being.
Low Glycemic Foods
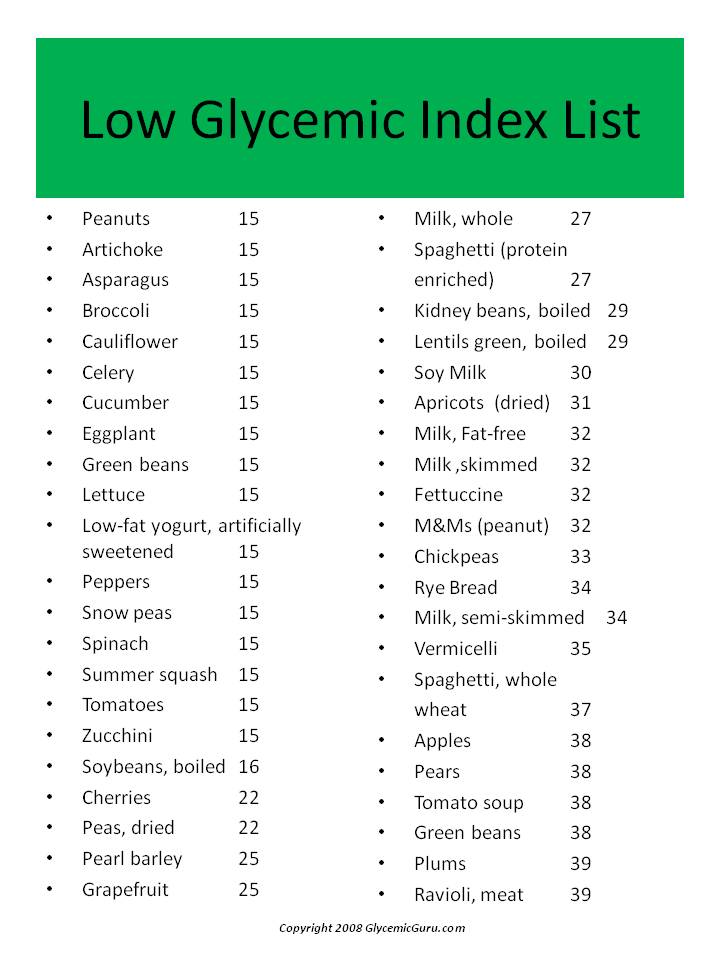
 Low glycemic foods are those that have a lower glycemic index value, meaning they have a slower and steadier effect on blood sugar levels. These foods are often rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Examples of low glycemic foods include most fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide sustained energy and a feeling of fullness, making them ideal for individuals seeking to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Low glycemic foods are those that have a lower glycemic index value, meaning they have a slower and steadier effect on blood sugar levels. These foods are often rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Examples of low glycemic foods include most fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide sustained energy and a feeling of fullness, making them ideal for individuals seeking to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
A low glycemic diet can also be beneficial for individuals with diabetes. By consuming foods that have a lower impact on blood sugar levels, individuals can better manage their blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications associated with high blood sugar.
The Role of the Glycemic Index in Weight Loss
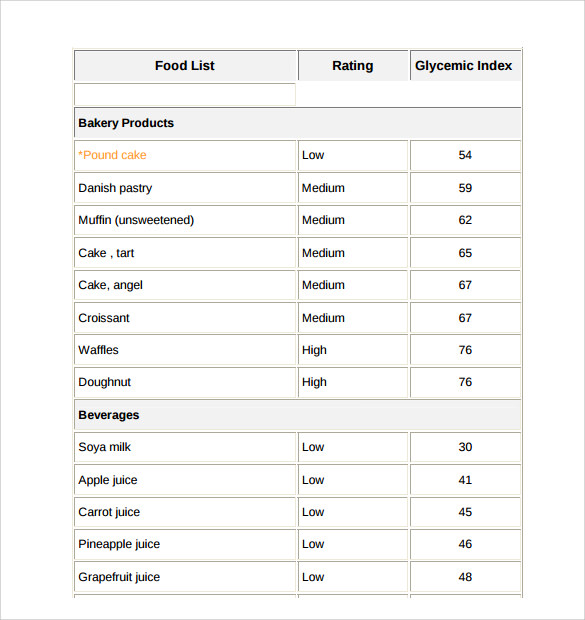 In addition to its impact on blood sugar levels, the glycemic index can also play a role in weight loss. Consuming low glycemic foods can help individuals feel fuller for longer periods, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy foods.
In addition to its impact on blood sugar levels, the glycemic index can also play a role in weight loss. Consuming low glycemic foods can help individuals feel fuller for longer periods, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy foods.
When individuals consume high glycemic foods, their blood sugar levels rise quickly, followed by a rapid drop. This can trigger hunger and cravings for more high glycemic foods, leading to a cycle of overeating and weight gain. By choosing low glycemic foods, individuals can stabilize their blood sugar levels and reduce the likelihood of cravings and excessive food intake.
Conclusion
 Understanding the glycemic index and referencing the glycemic index chart can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking to manage their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and make informed food choices. By choosing low glycemic index foods and incorporating them into a balanced diet, individuals can support their overall health and well-being.
Understanding the glycemic index and referencing the glycemic index chart can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking to manage their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and make informed food choices. By choosing low glycemic index foods and incorporating them into a balanced diet, individuals can support their overall health and well-being.
It’s important to note that while the glycemic index provides valuable information, it should not be the sole factor in determining a healthy diet. It’s important to consider other factors such as nutrient content, portion sizes, and overall dietary patterns when making food choices. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can also provide personalized guidance and support in managing blood sugar levels and overall nutrition.